-
School of Medicine
-
Educational Content
-
Prospective Students
-
Current Students and Alumni
International Affairs

-
Graduate School of Medicine
-
Educational Content
-
Prospective Students
-
International Affairs

-
Graduate School of Biomedical Science and Engineering
-
Educational Content
-
Prospective Students
-
Other

-
Faculty of Medicine
-
Organizational Structure
-
Industry-academia Cooperative Projects

-
Overview
-
Entrance Examinations
-
Publications and Promotional Material
-
Various Types of Data
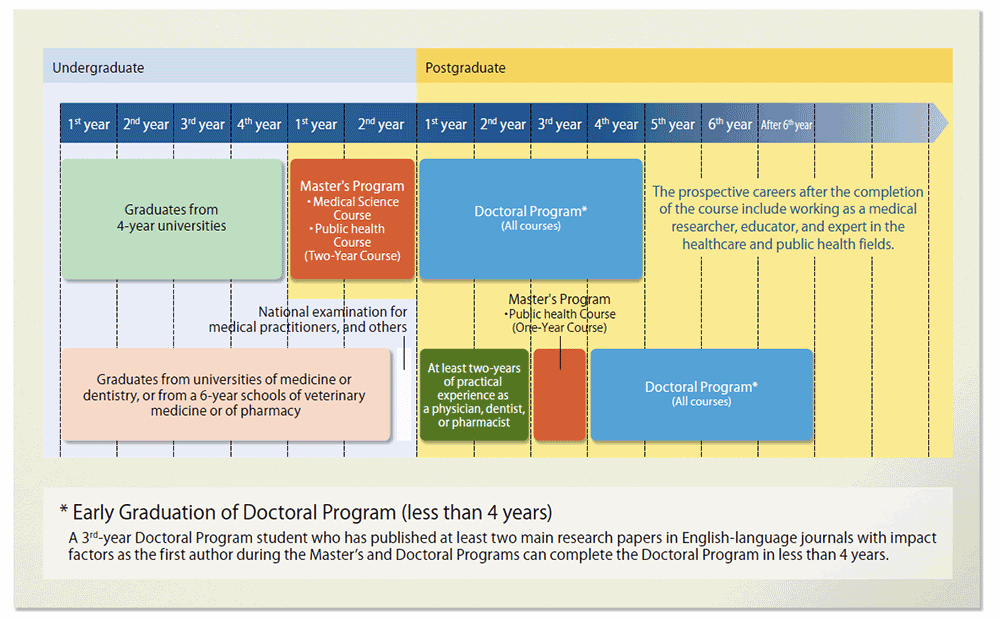
Master's Program
The 3 courses in the Master’s Program are outlined as follows.
- HOME
- Graduate School of Medicine
- Master's Program
Master's Program
Course Outline
Based on the “Educational Goals” of the Graduate School of Medicine, in the Master's Program, we aim to nurture individuals who have basic knowledge and skills to play active roles in their own field as (i) researchers and educators in the fields of medicine, life science and public health, (ii) highly specialized professionals in the fields related to medical care and public health, or (iii) experts in health services and health policy management. In order to nurture individuals who attain “Expected Competencies” , we offer interdisciplinary education beyond the boundaries of existing academic disciplines, aiming at the acquisition of basic knowledge and technology of mutually related fields. In addition, to nurture talented individuals responding to the diversified social needs, we introduce three types of coursework to study systematically through multiple subjects. Students choose the course that suits best to their purpose.
Medical Science Course
This course allows students to learn basic medicine research methods that provide the knowledge and skills required for medical research through experiential learning, as well as oral and written research presentation skills. Basic general medicine and basic medical research are offered to facilitate the development of specialists with the required extensive knowledge and skills.
Message from Graduate Student
Public Health Course
Public Health Course (Two-Year Course)
Public Health Course aims to develop human resources who are capable of playing active roles in addressing the challenges of public health with broad knowledge and high skills for the maintenance and improvement of the entire society and people's health, life and security.
Public Health Course (One-Year Course)
This course is intended for medical doctors (i.e. licensed physicians), dentists, pharmacist and other professionals with certain amount of practical experience, and aims to train, in one year, highly specialized professionals who play active roles in medical and public health fields.
This course will be established against the backdrop of growing public interest in health/medical problems and the aging and depopulation problems unique to Hokkaido, and provides education in five disciplines (Epidemiology, Biostatistics, Social and Behavioral Sciences, Health Services Administration, and Environmental Health Sciences) based on the essential criteria of the Council on Education for Public Health in the United States, thereby allowing students to acquire the extensive public health knowledge and skills necessary for highly specialized professionals.
Those who have chosen Public Health Course (either Two-Year Course or One-Year Course) should be affiliated with one Laboratory, selecting from Departments of Social Medicine Course.
※ Students should decide their preferred course during the application, and students will be allocated to either one- or two-year courses after the admission accounting for their preference. (Details will be informed after the admission.)
Message from Graduate Student
Message from Graduate Student
Obtainable degrees
- Medical Science Course
- Master of Medical Science
- Public Health Course
- Master of Public Health
※Students who enrolled before April of 2016 can earn only a master's degree (medical science).
Completion Requirements
Students are required to be enrolled in the Graduate School of Medicine for 2 years or more to
complete Medical
Science Course or Public Health Course (Two-Year Course), and for 1 year or more to complete
Public Health Course (One-Year Course).
Students should acquire 30 credits or more in majored fields, and pass the qualifying review and
examination of the Master's thesis or research achievements of specific assignment after receiving required research instruction from the supervisor.
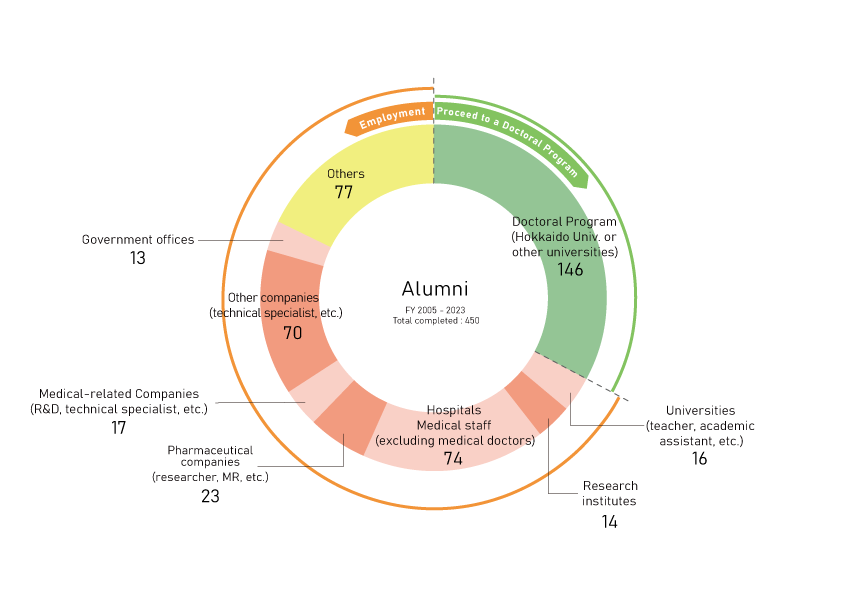
Career Options
After completing the Master’s Program, students can decide whether to enroll for the Doctoral Program, toward becoming highly skilled researchers or finding employment as medical professionals in society.
(As of May 2025)
Pursuing a doctorate
It is desirable that students who have completed their Master’s Programs pursue a doctorate, because they are still growing as students and researchers. Examination/admission fees are not required from students who continue their studies and research as doctoral students.
Message from a Graduate of the Master’s Program
Finding employment
Faculty members of the Graduate School of Medicine help students find employment.
| Positions | Businesses | |
|---|---|---|
| Employment options for specialists |
|
|
Message from a Graduate of the Master’s Program
Long-Term Study Program
(NOT eligible for Public Health Course (One-Year Course))
1. Purpose
The standard term is two years. Long-Term Study Program (longer than two years) is offered for those who wish to study and acquire a degree through a long-term enrollment due to time limitations. Applicants are individually screened for eligibility.
2. Eligibility
Those who have difficulties in completing the program within the standard term due to personal reasons such as (1) full time jobs, (2) part time jobs (3) child-raising or a long-term nursing care, or (4) visual disabilities, auditory disabilities, physical disabilities or other disabilities are eligible to apply for this program.
3. Period of Enrollment
Students in Master’s program may extend their term of study up to four years, and extension of study term can be applied by the year as a unit. Students in Master’s Program are allowed to stay enrolled up to two years in addition to the period approved for a Long-Term Study Program.
Students in a Long-Term Study Program are allowed to have two years leave as well as regular students.
4. Application Procedure
- (1)
- Application Period
Please request at the time of application for admission. Application form is available at Student Affairs Office of the Graduate School of Medicine. - (2)
- Application Documents
Please submit the following documents to Student Affairs Office of the Graduate School of Medicine.- i) Application for the Long-Term Study Program (Form 1-1)
- ii) Reasons to apply the Long-Term Study Program (Form 2)
- iii) Study plan of the Long-Term Study Program (Form 3)
- iv) Documents proving the need for the long-term study program
5. Shortening or re-extension of Long-Term Study Program
When deemed necessary by the Graduate School of Medicine, study term of Long-Term Study Program could be either shortened or re-extended once during the program.
Please contact Student Affairs Office of the Graduate School of Medicine for further information.
6. Tuition Fees *
Annual tuition fee of the Long-Term Study Program is determined by dividing the total fees paid for the regular program of standard term (annual fee×2 years) by the number of years allowed for the Long-Term Study Program. Tuition fee is non-refundable, and the tuition already been paid will not be adjusted.
* Please do NOT pay tuition fee of the long-term study program before receiving a notice of determination.
Course Guidance
The following 4 subjects are offered in the Master's Program in Medical Science.
- Required Core Subjects (Kyoutsu Koa Kamoku)
- Required Subjects I (Hisshu Kamoku I)
- Required Subjects II (Hisshu Kamoku II)
- Elective Subjects (Sentaku Kamoku)
Public Health Course provides 5 discipline areas of education (Epidemiology, Biostatistics, Social and Behavioral Sciences, Health Services Administration and Environmental Health Sciences) which are set as essential requirements by accreditation criteria of the Council on Education for Public Health in the United States. Students learn basic subjects at Required Subjects I that allow them to acquire minimum knowledge and capability that are required for public health experts. Required Subjects I will be conducted under the interdisciplinary educational system, offered by lecturers with a broad background, including specialists in medicine, science and engineering, and humanities and social sciences. “Elective Subjects” are offered to additionally cultivate expertise broaden the understanding of various public health issues, and build up the capacity of gathering information and proper judgement.
Required Core Subjects (Kyoutsu Koa Kamoku)
| Course | Subject | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Science Course Public Health Course (Two-Year Course) Public Health Course (One-Year Course) |
Introduction to Basic Medical Research | 1 |
| Basic Experimental Methods and Research Designs | 1 | |
| Introduction to Medical Ethics | 1 | |
| Introduction to Translational Research | 1 |
Required Subjects I (Hisshu Kamoku I)
| Course | Subject | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Science Course | Basic Research Methods in Medical Sciences I | 1 |
| Basic Research Methods in Medical Sciences II | 1 | |
| Public Health Course (Two-Year Course) |
Basic Epidemiology | 1 |
| Basic Biostatistics | 1 | |
| Basic Social and Behavioral Sciences | 1 | |
| Basic Health Services Administration | 1 | |
| Basic Environmental Health Sciences | 1 | |
| Introduction to Basic Medicine | 1 | |
| Introduction to Clinical Medicine | 1 | |
| Public Health Course (One-Year Course) |
Basic Epidemiology | 1 |
| Basic Biostatistics | 1 | |
| Basic Social and Behavioral Sciences | 1 | |
| Basic Health Services Administration | 1 | |
| Basic Environmental Health Sciences | 1 |
Required Subjects II (Hisshu Kamoku II)
| Course | Subject | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Science Course | Scientific Presentation and Communication | 1 |
| Presentation Skills I | 1 | |
| Presentation Skills II | 2 | |
| Master's Thesis Research in Medical Sciences | 10 | |
| Public Health Course (Two-Year Course) |
Scientific Presentation and Communication | 1 |
| Presentation Skills I | 1 | |
| Presentation Skills II | 2 | |
| Master's Thesis Research in Public Health | 10 | |
| Public Health Course (One-Year Course) |
Presentation Skills I | 1 |
| Presentation Skills II | 2 | |
| Master's Thesis Research in Public Health | 10 |
Elective Subjects (Sentaku Kamoku)
| Course | Subject | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Science Course | Basic Principles of Medicine | [2] |
| Introduction to Clinical Genomics | 2 | |
| Biomedical Informatics | 1 | |
| Clinical Epidemiology | 2 | |
| Clinical Sequence Technique | 2 | |
| Clinical Pathology and Laboratory Medicine | 1 | |
| Introduction to Basic Medicine | 1 | |
| Introduction to Clinical Medicine | 1 | |
| Required Subjects I and Required Subjects II of Public Health Course (EXCEPT Master's Thesis Research in Public Health) | ||
| Public Health Course (Two-Year Course) Public Health Course (One-Year Course) |
※Advanced Epidemiology | [1] |
| ※Advanced Biostatistics | [1] | |
| ※Advanced Social and Behavioral Sciences | [1] | |
| ※Advanced Health Services Administration | [1] | |
| ※Advanced Environmental Health Sciences | [1] |
※As for the subject which credit number is indicated as [number], students can take multiple choices as far as the chosen subjects belong to different subject titles.
How to take subjects
- Medical Science Course
- Take 4 credits from Required Core Subjects, 2 credits from Required Subjects I, 14 credits from Required Subjects II, and 10 credits or more including Basic Principles of Medicine offered by belonging laboratory from Elective Subjects.
- Public Health Course
(Two-Year Course) - Take 4 credits from Required Core Subjects, 7 credits from Required Subjects I, 14 credits from Required Subjects II and 5 credits or more from subjects with ※.
- Public Health Course
(One-Year Course) - Take 4 credits from Required Core Subjects, 5 credits from Required Subjects I, 13 credits from Required Subjects II and 8 credits or more from subjects with ※.