-
School of Medicine
-
Educational Content
-
Prospective Students
-
Current Students and Alumni
International Affairs

-
Graduate School of Medicine
-
Educational Content
-
Prospective Students
-
International Affairs

-
Graduate School of Biomedical Science and Engineering
-
Educational Content
-
Prospective Students
-
Other

-
Faculty of Medicine
-
Organizational Structure
-
Industry-academia Cooperative Projects

-
Overview
-
Entrance Examinations
-
Publications and Promotional Material
-
Various Types of Data
Course Guidelines
- HOME
- School of Medicine
- Course Guidelines
From Enrollment to Graduation
The six-year period from enrollment in the school of medicine till graduation is divided into following four courses:
Studies at the school of medicine start from acquiring a general wide view and converge to improving expertise. The details of each course are as follows.
1. Liberal Education Course for Medical Students
Medicine is a part of the natural sciences. However, physicians need a broad knowledge of their fellow human beings and a positive understanding attitude to interact with patients and their families who may have different ideas and values. This is why it is stated that “medicine is a part of the liberal arts field.”
In the first year of the study at the school of medicine, students are assigned to take courses in the general educational department. This is an important period where students cultivate and develop a broad outlook, build strong and deep human relationship, and lay the foundations for the study as medical student and for the all life study in general arts with students of other science faculties of the university.
The study of liberal arts and scientific subjects other than medicine may seem unrelated to the study of medicine; however they serve as a driving force enriching the imagination and creativity encouraging the development of the broad understanding of the world that is necessary to conduct research and provide medical care.

Freshmen Guidance
During the guidance session held for all students in April, explanations are given on how to take courses and about university life. The guidance session for freshmen at the School of Medicine includes introductions to the history of the school and the curriculum for the next six years.

Classes for general education subjects are held at the Institute for the Advancement of Higher Education located near the School of Medicine building.
2. Basic Medicine Course
Illness is the state where the normal functioning of the body has changed and the understanding of illness is undergirded by an understanding of the normal state. This course lasts one and a half years from the 1st semester of the second year to the 1st semester of the third year. Here the study starts from the normal structure and functions of the human body (anatomy, histology, Imaging anatomy, physiology), and enables an understanding of biological phenomena from the molecular and gene level (biochemistry, pharmacology). Next, students are acquainted with the basic processes in which humans change from the normally functioning state to illness and diseases (microbiology, immunology, pathology, basic application of oncology).
Students also learn subjects classified in the category of social medicine that approaches the health and illness of humans from the viewpoints of interactions among groups of human, environmentally induced problems, societal structures, and prevention (hygieiology, public health study, forensic medicine).
All of the medically oriented specialty subjects that are introduced from the start of the Basic Medicine Course are required subjects and the syllabus is very concentrated.

Students' Association Forum for sophomores
A guidance session for promotion to the Basic Medicine Course (for sophomores) is held in early April.
After an address by the dean of the School of Medicine and a guidance session for the Medical Course, the Students’ Association Forum is held.

Image of an experiment on pathology
3. Clinical Medicine Course
The Clinical Medicine Course offers study of the particulars of a variety of illnesses and diseases. Students study illnesses and diseases multi-dimensionally and learn the foundations of clinical medicine including internal medicine, surgery, and specialized medicine. Students acquire the basic skills necessary to understand disease conditions, laboratory findings, diagnosis, and medical treatment with a thorough understanding of patients as human beings with emotions. This understanding is very important for the next step in the study, the Clinical Clerkship Course, where students will face actual patients.
The Clinical Medicine Course includes a one-month medical research practicum, which functions as the introductory task for medical research. Here, students are assigned to work in a laboratory, to be researchers of basic medicine and research physicians learning experimental methods and ways of thinking.
At the end of the Clinical Medicine Course students have to take common achievement tests, CBT (computer based testing), which measures the knowledge and degree of comprehension, and Pre-CC OSCE (pre-clinical clerkship objective structured clinical examination), which measures skills in medical interviews (clinical history recording) and consultation. Students must pass these tests before they can proceed to the Clinical Clerkship Course.
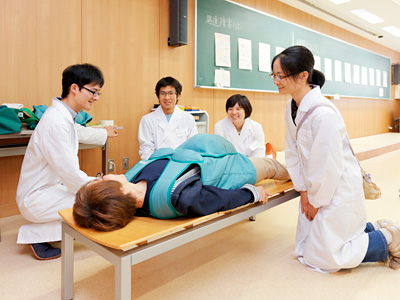
Medical Festival where daily study outcomes are introduced
At the Medical Festival held during the Hokkaido University Festival every year, seniors and others serving as project heads take the lead in offering guidance on emergency actions and pregnancy and wheelchair experiences to general citizens.

4. Clinical Clerkship Course
This course is where the clinical clerkship starts.
In the second semester of the fourth year, students are assigned to different clinical
departments in Hokkaido University Hospital and acquire practical skills based on the study
that they have been exposed to in each of the previous courses while interacting with
patients and medical staff in the clinical setting, the hospital. Along with this practical
training, students review problems and questions they have become aware of through their training in united clinical lectures, and learn the basics of general practice skills. Training in social medicine is also conducted at this time.
For the 6 months of the 2nd semester of the 5th year, students must participate in 6 four-week clinical clerkship programs in core clinical departments at Hokkaido University Hospital and at outside medical institutions.
In the 1st semester of the 6th year, students must participate in 3 clinical attachments (4 weeks per clinical department or per field).
Before finishing the Clinical Clerkship Course, students must attend lectures in clinical pathology and interprofessional/simulation trainings. Through this training students acquire practical skills that will be useful after graduation.
At the end of this course, the Post-Clinical Clerkship Objective Structured Clinical Examination (Post-CC OSCE) is conducted as part of the graduation examination to evaluate clinical skills and attitudes. Students must then take the National Examination for Medical Practitioners, and will become registered physicians after they have passed this examination.
All the subjects of the specialized education of the school of medicine are required subjects. This is a clear difference from the requirements in other fields and faculties. The reasons for this requirement are the social demands on physicians, who are responsible for the lives of patients. Therefore, students are required to study all the subjects and basics that are required of a physician during the six years of the education in the faculty. This makes for a concentrated course.

Ceremony for the Commencement of Bachelor of the School of Medicine following the six-year course of study
Following their six-year course of study, students attend this ceremony with a sense of fulfillment. After the ceremony, students spread their wings and join medical facilities, universities, research institutions, and other organizations.
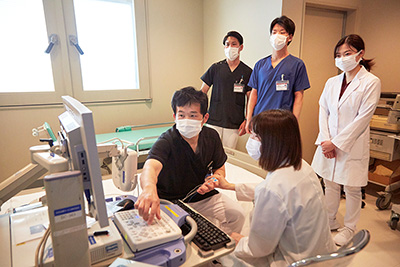
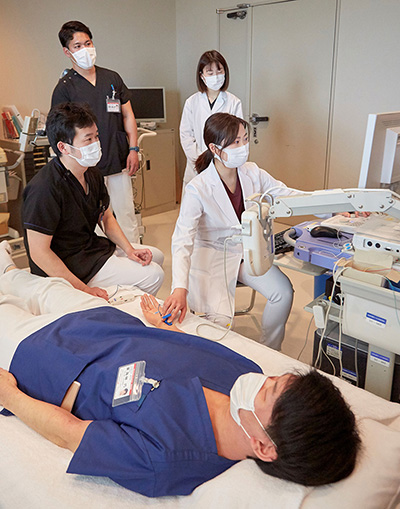
Clinical training at all departments: Electrophysiology training at the Department of Neurological Medicine
Similarly, each medical department also provides highly specialized training.
Future Directions
Even after passing the final national examination, graduates do not become full-fledged physicians. After graduation physicians will be working in either of the following capacities: (1) researcher, educational research instructor, (2) clinical physician and medical specialist, (3) work in medical administration. The study to qualify for either of these will start after the graduation. Specifically the study and learning for the case of (1) and (2) are conducted in relation with the university and fundamental study will continue for ten years after graduation.
To become (1) a researcher and educational research instructor, and (2) an efficient medical specialist, it will be necessary to enroll in a graduate school and there acquire research skills. Today, physicians are required to be qualified medical specialists. Therefore, each graduate will need to acquire research skills to able to play a leading role as an efficient medical specialist in the community. The best way to acquire these research skills is to study in a graduate school. Hokkaido University offers graduate students and interns a unique and distinct curriculum that meets their learning goals after graduation.
Finally, physicians always have to update and renew their knowledge and skills because of their responsibilities to patients and society. Therefore, it is important for students of the medical faculty to be prepared to keep studying and learning throughout life.